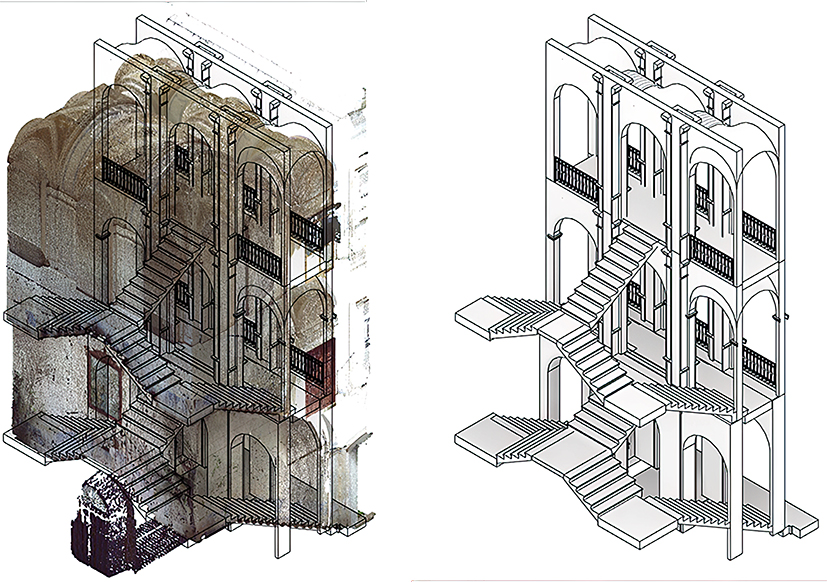
A point cloud classification method for the Scan-to-BIM process in Architectural Heritage
Abstract
Heritage Building Information Modelling (H-BIM) has completely changed the meaning of managing architectural sites and ancient buildings. Nowadays, the application of cutting-edge methods for analysis, conservation and restoration is made possible by the modern 3D scanning technologies, such as terrestrial laser scanners (TLS) and digital cameras, which produce highly accurate point clouds. Furthermore, as these files are time-consuming and computationally expensive, strategies are being developed to optimise their handling and to streamline the conversion of a point cloud into a BIM model, adopting Scan-to-BIM approaches and widespread Artificial intelligence.
In this scenario, the current work investigates the use of the CANUPO multiscale algorithm and the RANSAC model-fitting method for the classification of the staircase of Palazzo Nico, a neoclassical building in Gioia del Colle, Italy, using data obtained through TLS. The location’s geometry, which includes numerous floors, vaults, balustrades, and typical 19th-century-style ornate staircase, makes it an excellent case study for assessing the applicability of these tools, serving as a source base for additional modelling procedures.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.20365/disegnarecon.30.2023.20
Keywords
Full Text:
PDFRefbacks
- There are currently no refbacks.
Copyright (c) 2023 Riccardo Tavolare
DISEGNARECON
ISSN 1828 5961
Registration at L'Aquila Law Court no 3/15 on 29th June, 2015.
Indexed in SCOPUS. Diamond Open Access. All papers are subjected to double blind peer review process by qualified reviewers.
Journal founded by Roberto Mingucci
